API REST Pagination
Pagination is a strategy that limits access to large datasets by dividing the data into manageable chunks or "pages." This approach provides mechanisms for accessing subsequent or previous pages of data.
When dealing with API responses that could potentially return large datasets, pagination becomes essential for two main reasons:
-
Mitigate data access abuse: Pagination limits the amount of data that can be accessed in a single request. Clients or consumers can only retrieve a defined subset of data per page, preventing potential system overload or abuse.
-
Improve response performance: By returning smaller sets of data, pagination ensures faster response times. This is particularly beneficial when dealing with large datasets, as it reduces the load on both the server and the client.
Ory supports two pagination strategies:
- Token-based pagination: The primary and recommended method for paginating through data in Ory's API.
- Offset pagination: A deprecated method that is still supported but not recommended for new implementations.
In the following sections, we'll explore each of these pagination strategies in detail, with a focus on the recommended token-based approach.
Token pagination
Ory implements token-based pagination as the primary method for handling large datasets in list operations. This approach offers better performance and consistency compared to traditional offset-based pagination.
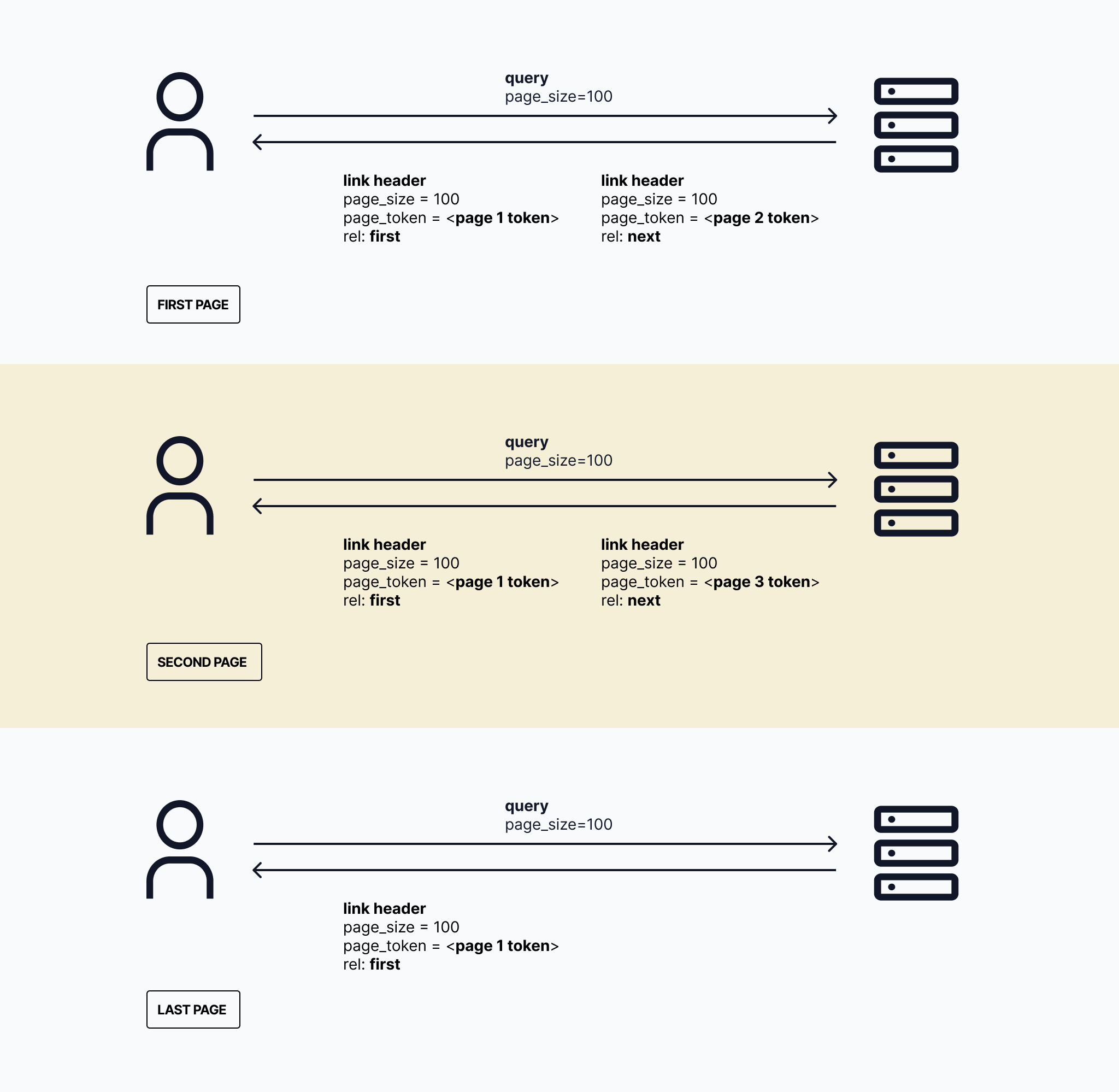
Pagination parameters
Ory uses two parameters to paginate through data:
page_size: Determines the number of items returned per page.page_token: Acts as a pointer to a specific page in the dataset.
How it works
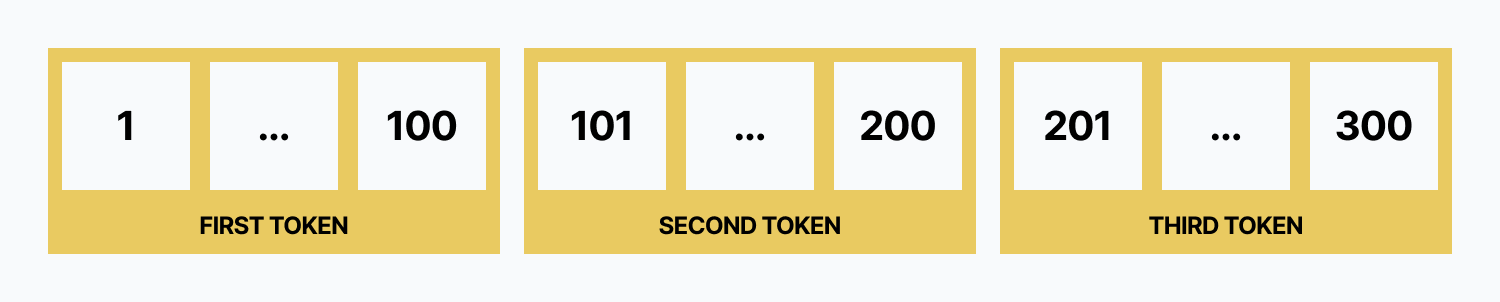
Let's walk through an example to illustrate how token pagination works in Ory:
Imagine you have 300 customers in your Ory project, and you want to list them 100 at a time.
-
Initial request: Set the
page_sizequery parameter to 100 for your first request:GET https://$PROJECT_SLUG.projects.oryapis.com/admin/identities?page_size=100
Authorization: Bearer $ACCESS_TOKEN -
Response: You'll receive a response payload containing the first 100 customers. Additionally, the response header will include a
linkheader with details about the first and next pages:link:
</admin/identities?page_size=100&page_token=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000>; rel="first",
</admin/identities?page_size=100&page_token=30f8507f-40e6-44b9-924f-5f814e3f072e>; rel="next" -
Understanding the Link Header:
- The
firstlink always points to the first page of results. Its token (in this case,00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000) remains constant. - The
nextlink points to the next page of results. Its token (e.g.,30f8507f-40e6-44b9-924f-5f814e3f072e) is unique and changes with each page.
- The
-
Subsequent requests: To retrieve the next page, use the
nexttoken in your follow-up request:GET https://$PROJECT_SLUG.projects.oryapis.com/admin/identities?page_size=100&page_token=30f8507f-40e6-44b9-924f-5f814e3f072e
Authorization: Bearer $ACCESS_TOKEN
Best practices
- Always use the tokens provided in the
linkheader for navigation. Do not attempt to generate or modify these tokens yourself. - If you need to start from the beginning, use the
firstlink or omit thepage_tokenparameter. - Keep track of the previous/current
nexttoken to allow for backward pagination through your results. - Be prepared for the maximum
page_sizeto change. Your implementation should handle such changes gracefully. - Do not attempt to reverse engineer or make assumptions about the
page_tokenformat, as it may change without notice. Always treat it as an opaque string.
By leveraging token-based pagination, you can efficiently navigate through large datasets in Ory, ensuring consistent and performant data retrieval.
Usage examples
The following examples demonstrate how to use token-based pagination with Ory's SDKs in Python and Ruby.
Scenario 1: Python SDK
This example shows how to fetch a single page of identities using the Python SDK:
import os
from pprint import pprint
from ory_client.api_client import ApiClient
from ory_client.configuration import Configuration
from ory_client.api.identity_api import IdentityApi
# Configure your Ory credentials
configuration = Configuration(
access_token="{API_KEY}",
host="https://{PROJECT_SLUG}.projects.oryapis.com",
)
# Enter a context with an instance of the API client
with ApiClient(configuration) as api_client:
# Create an instance of the API class
api_instance = IdentityApi(api_client)
try:
# List Identities
api_response = api_instance.list_identities(
page_size=1,
page_token="<token>",
)
pprint(api_response)
except Exception as e:
print("Error fetching identities: %s\n" % e)
Key points:
- Replace
{API_KEY}with your actual Ory API key. - Replace
{PROJECT_SLUG}with your Ory project slug. - The
page_sizeis set to 1 for demonstration purposes. Adjust this value based on your needs. - Replace
<token>with the actual page token received from a previous request, or omit it for the first request.
For more details, see the IdentityApi list documentation.
Scenario 2: Ruby SDK
This example demonstrates how to fetch a single page of identities using the Ruby SDK:
require 'ory-client'
# Configure your Ory credentials
OryClient.configure do |config|
config.host = 'https://{PROJECT_SLUG}.projects.oryapis.com'
config.access_token = '{API_KEY}'
end
# Create an OryClient instance
api_instance = OryClient::IdentityApi.new
opts = {
page_size: 1,
page_token: '<token>'
}
begin
# List Identities based on pagination
result = api_instance.list_identities(opts)
p result
rescue OryClient::ApiError => e
puts "Error fetching identities: #{e}"
end
Key points:
- Replace
{PROJECT_SLUG}with your Ory project slug. - Replace
{API_KEY}with your actual Ory API key. - The
page_sizeis set to 1 for demonstration purposes. Adjust this value based on your needs. - Replace
<token>with the actual page token received from a previous request, or omit it for the first request.
For more information, refer to the IdentityApi list documentation.
Offset pagination (Deprecated)
Offset pagination is deprecated. It is strongly recommended to use Token pagination instead.
While not recommended for new implementations, Ory still supports offset-based pagination for backwards compatibility. This method allows you to paginate through data using an offset and a page size.
How it works
Offset pagination uses two query parameters:
per_page: The number of items you want for each page.page: The page number you want to retrieve (starts at 0).
Example usage
Let's consider a scenario where you have 300 customers and you want to retrieve customers 101 to 200:
GET https://{PROJECT_SLUG}.projects.oryapis.com/admin/identities?per_page=100&page=2
Authorization: Bearer {YOUR_API_KEY}
In this example:
per_pageis set to 100, indicating you want 100 items per page.pageis set to 2, which will return items 201-300.
Migrating to token pagination
If you're currently using offset pagination, it's highly recommended to transition to token-based pagination. Refer to the Token Pagination section for implementation details and best practices.
Handling pagination errors
Ory typically returns a 400 Bad Request error for pagination-related issues. Here's an example of an error response when supplying an invalid token:
{
"error": {
"code": 400,
"status": "Bad Request",
"request": "38308051-dd5e-9f91-b053-5b32f751b281",
"reason": "The page token is invalid, do not craft your own page tokens",
"message": "The request was malformed or contained invalid parameters"
}
}
Key fields in the error response:
code: The HTTP status code (e.g., 400 for Bad Request)status: A text representation of the HTTP statusrequest: A unique identifier for the request, useful for troubleshootingreason: A specific description of what went wrongmessage: A general error message